Erectile Dysfunction
Introduction to Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient enough to have satisfying sexual intercourse. It is one of the most commonly untreated medical disorders in the US, with roughly 30 million men reporting problems achieving or maintaining an erection. Yet, only 10% of men ever seek treatment or ask about options. Erectile dysfunction is associated with depression, loss of self-esteem, and anxiety. It can also be associated with chronic medical conditions such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes.
Dr. Osterberg Discusses What Is ED?
What is Erectile Dysfunction?
Anatomy
The penis is composed of two erectile bodies and the urethra. Penile erection is a result of a complex interaction between the brain and increased blood flow to the penis. Any disease that impacts the nervous system or blood vessels can impact erectile function.
Causes of Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (ED) occurs for many reasons, all of which ultimately relate back to blood flow and the nervous system. Approximately 90% of all erectile dysfunction can be traced back to an organic cause. The majority of the time, this is due to either inadequate blood flow inward to the erectile bodies or a leakage of blood out from the erectile bodies. Difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection may be an underlying sign of more systemic problems, such as diabetes, heart disease, or high cholesterol. Therefore, the quality of erections may be seen as a window into your overall health. In fact, men with heart disease are 50x more likely to have ED compared to men without heart disease. Similarly, roughly 20% to 75% of men with diabetes have ED. Medications such as SSRI and beta-blockers are associated with ED. Prior surgery or radiation to the organs within the pelvis, specifically the prostate, may lead to ED.
Work-up and Evaluation
A thorough history and physical is the mainstay of an Erectile Dysfunction work-up and evaluation. Dr Osterberg and his team will request you fill out a Sexual Health Inventory for Men (SHIM) questionnaire. This helps us quantify and ascertain the degree of your ED and how it impacts your quality of life. Complete medical history, active medication list, prior surgical history, smoking history, and family history of medical conditions will all be obtained.
Treatment options for ED
Medical Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction
Oral Medications. Initial treatment for ED is with medications. Cialis (Tadalafil), Levitra (Vardenafil), and Viagra (Sildenafil) work by selectively inhibiting an enzyme in the penis called Phosphodiesterase V (PDE V), a chemical that takes away the erection. They are all in a family of medication called PDE5 inhibitors. Ultimately, they work by increasing levels of cyclic GMP, which allows for increased penile blood flow. There are subtle differences between the medications available; however they all work in a similar fashion.
For example, the half-life of Cialis is much longer and therefore it may allow for more spontaneity. Common side effects of the medication include flushing, vision changes, nasal congestion, and decreases in blood pressure. If the patient has extensive cardiac history, consultation with a cardiologist may be necessary to ensure the individual is safe for sexual activity. Despite being efficacious, oral phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors may have limited benefit in men with severe erectile dysfunction, diabetics, or men who have had injury to the pelvic nerves responsible for erections.
Injection Therapy. In men who are dissatisfied with their response to oral phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors, another treatment option is penile injections, also known as intracavernosal injections (ICI). CaverjectTM or EdexTM (Alprostadil) is injected directly into the side of the penis and produces an erection. The medication dilates the arteries of the penis and allows blood to flow in. An erection occurs anywhere from 5 to 15 minutes after injection. Dr. Osterberg will teach you how to administer your injection and help you decide on a dosage that suits your needs. The number of injections is not to exceed 12 each month, and should be spaced out as evenly as possible. The site of injection should alternate between left and right side of the penis. The most common side effect of injection therapy is a aching feeling in the penis that will ultimately go away with time. If this ache is particularly painful, Dr. Osterberg may recommend a combination of medications called TriMix - Papaverine, Phentolamine, and Alprostadil. Occasionally, ICI may cause a painful, sustained, prolonged erection, known as priapism. Priapism (a rigid erection for more than 4 to 8 hours) requires immediate medical attention, but is easily reversed when treated early.
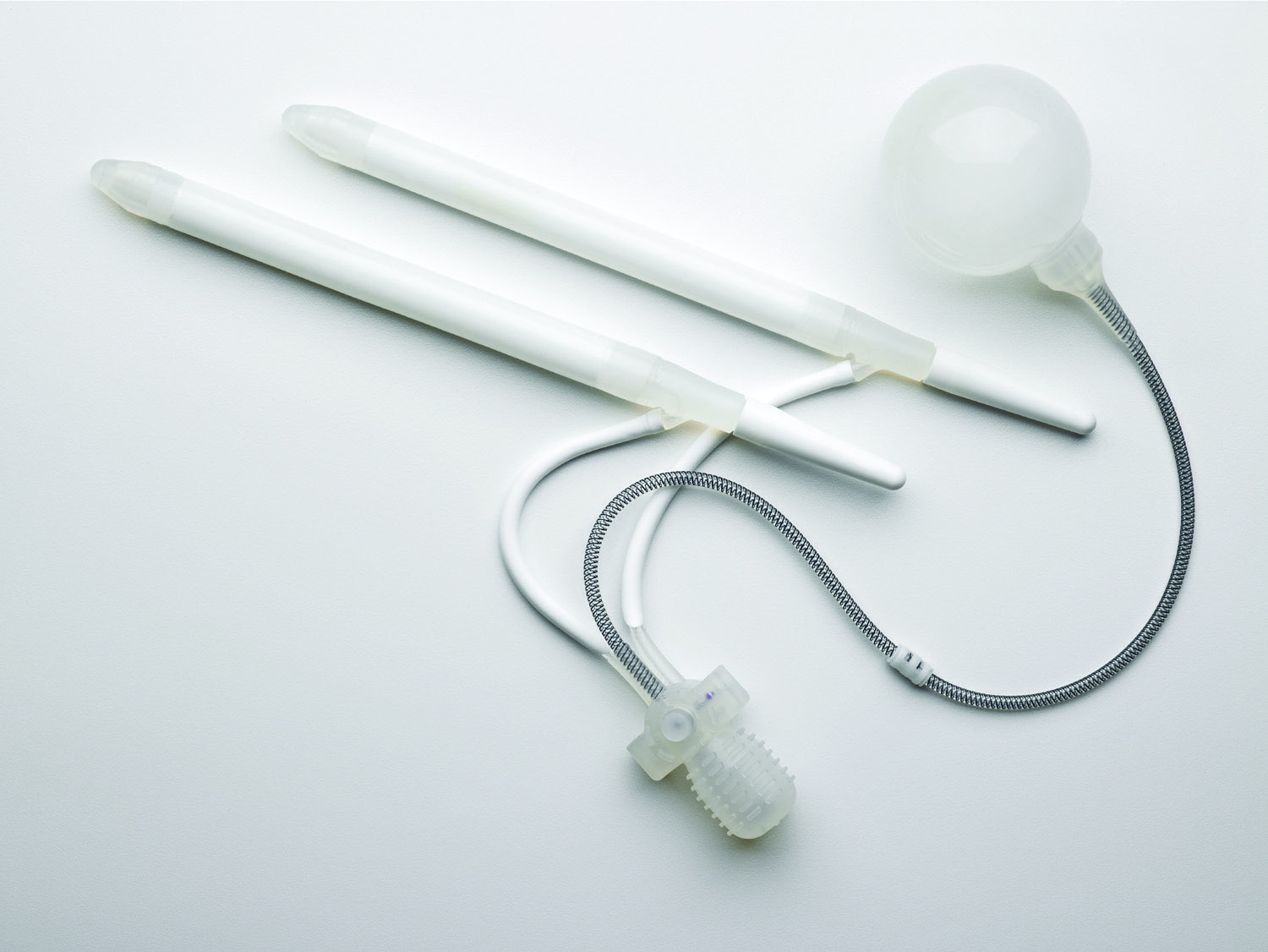
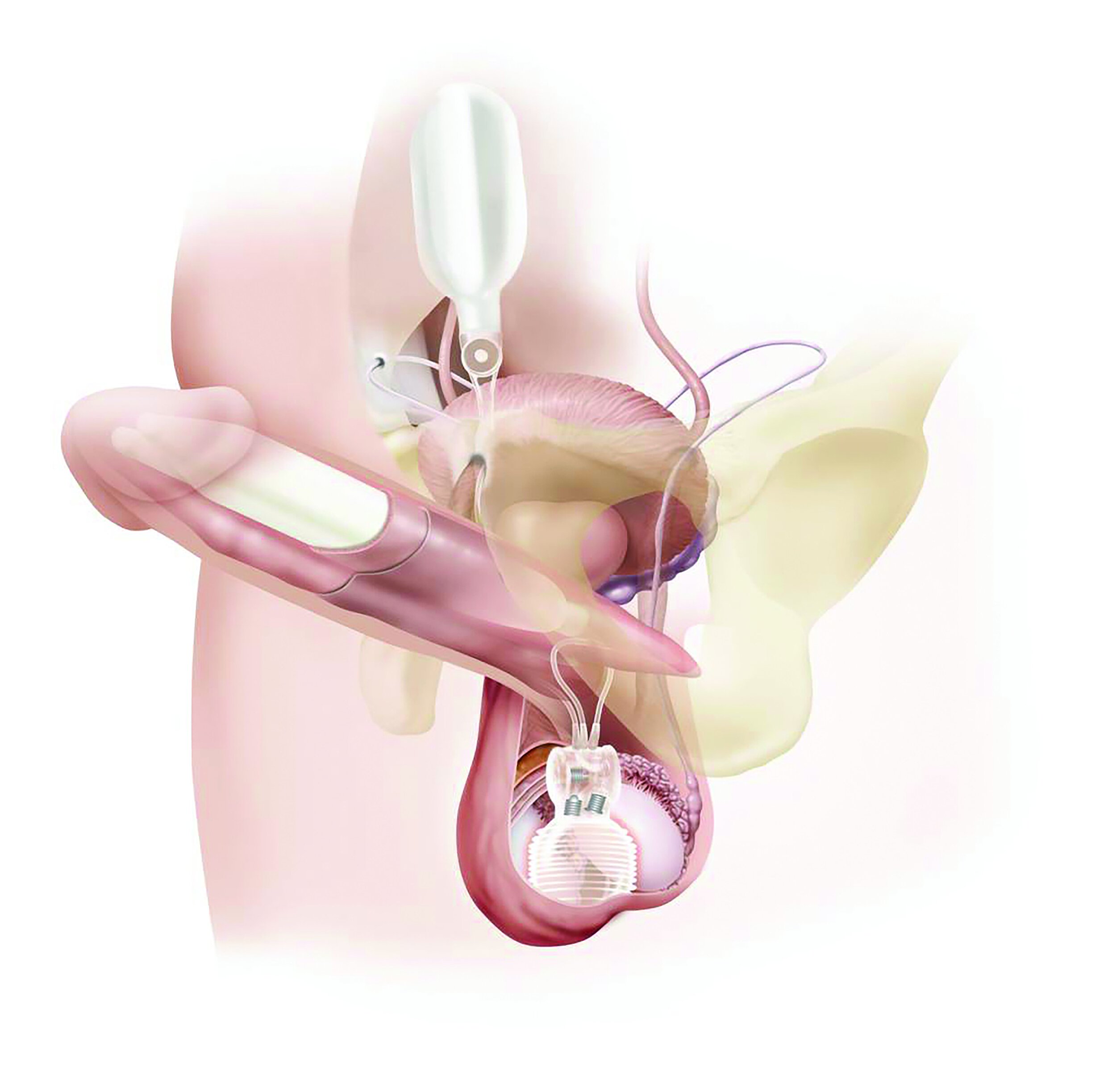
Penile Implant Surgery. A penile implant is used to treat impotence (not able to have or keep an erection) in men. This is also called erectile dysfunction (ED). Implants are used in men who have not responded to other treatments for ED. Implants are also used in men who have responded to these treatments, but who don’t like the side effects. There are several types of penile implants that Dr. Osterberg will review with you. The most commonly placed penile implant is a 3 piece inflatable device. The device is composed of 3 pieces: A scrotal control pump, a reservoir, and erectile cylinders. When the patient is ready, he presses the control pump, which moves fluid from the reservoir into the erectile cylinders, ultimately achieving a firm erection. This device allows for the past flaccidity of the penile shaft when not in use and is most comfortable for patients. The three-piece prosthesis provides the best cosmetic result and is totally concealed within the body. Because it relies on a pump placed in the scrotum, it is prone to device malfunction and failure over time. The life expectancy of a three-piece penile prosthesis ranges from 5-20 years. When the device fails, it can be easily replaced.
What is a penile implant?
Coloplast Titan Touch Penile Prosthesis